Vascular Malformations: Understanding Abnormal Blood Vessel Networks
Vascular malformations are abnormal clusters or networks of blood vessels that are present from birth and grow slowly over time. They may involve arteries, veins, capillaries, lymphatic vessels, or a combination of these. While some vascular malformations remain silent for years, others can cause pain, swelling, cosmetic concerns, bleeding, or functional problems depending on their size and location. Early evaluation by a vascular specialist helps in planning safe and effective treatment.
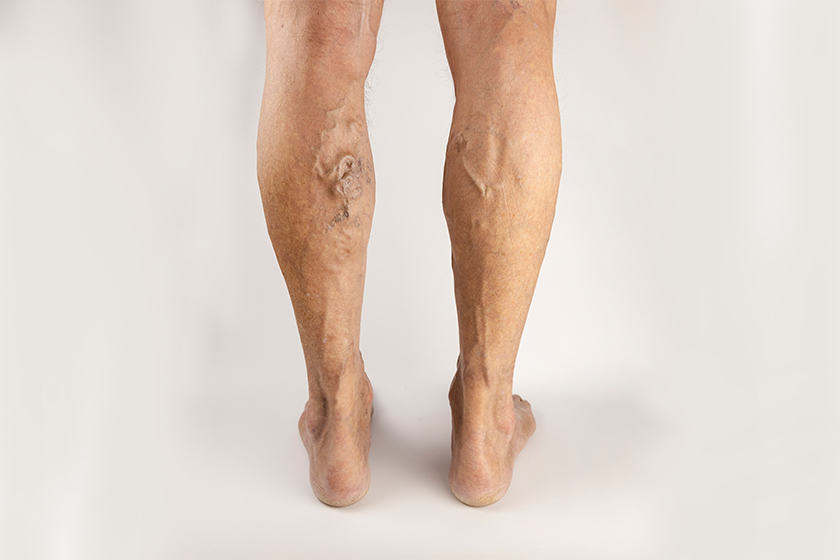
Types of Vascular Malformations
Vascular malformations are classified based on the type of vessels involved and the speed of blood flow:
- Venous Malformations: Abnormally formed veins that can cause pain, swelling, and bluish discoloration.
- Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs): Direct connections between arteries and veins, often high-flow and potentially serious.
- Lymphatic Malformations: Abnormal lymphatic channels or cysts leading to swelling and fluid collections.
- Capillary Malformations: Superficial vessel changes often seen as birthmarks or skin discoloration.
- Combined Malformations: Involving more than one type of vessel (e.g., veno-lymphatic or arterio-venous).
Common Symptoms and Concerns
- Localised swelling or a soft lump that may enlarge over time.
- Pain, heaviness, or discomfort in the affected area.
- Skin colour changes, visible veins, or bluish patches.
- Recurrent bleeding, ulceration, or infection over the lesion.
- Functional limitations, deformity, or cosmetic concerns.
Diagnosis of Vascular Malformations
A detailed clinical assessment is combined with imaging to understand the type, extent, and flow characteristics of the malformation:
- Doppler ultrasound to assess blood flow patterns.
- CT or MR angiography to map the vessels and surrounding structures.
- MRI to evaluate soft tissue involvement and depth.
- Conventional angiography for high-flow AVMs requiring intervention.
Treatment Options
Treatment is individualised based on symptoms, location, and type of vascular malformation:
- Sclerotherapy: Injection of a special medicine into the malformation to shrink or close abnormal vessels.
- Embolisation: Blocking abnormal blood flow using coils, glue, or particles, often for AVMs.
- Laser or Local Therapies: For superficial skin lesions and cosmetic improvement.
- Surgical Removal: In selected cases where the malformation is well-defined and accessible.
- Combined Approaches: Using endovascular, sclerotherapy, and surgery together for complex lesions.
Why Timely Evaluation Is Important
Although many vascular malformations are benign, they can enlarge, bleed, or cause functional and cosmetic problems over time. Early diagnosis helps prevent complications, reduce symptoms, and improve appearance and quality of life. Modern minimally invasive techniques make treatment safer and more precise than ever before.
Our vascular team offers comprehensive assessment and advanced treatment options for venous, lymphatic, and arteriovenous malformations. If you or your child has a persistent swelling, birthmark-like lesion, or suspected vascular malformation, schedule a consultation for expert guidance and a personalised care plan.
Vascular Specialist in BTM Layout – Expert Vascular Care
Our Vascular Specialist in BTM Layout provides expert diagnosis and treatment for arterial and venous conditions. Using advanced imaging and minimally invasive endovascular procedures, we ensure safe and effective care for varicose veins, aneurysms, and peripheral artery disease. Trust Sugathi Liver & Vascular Clinic for personalized vascular care with optimal recovery and long-term outcomes.
More Services
- Understanding Varicose Veins
- Lower Limb Arterial Diseases (PAD)
- Endovascular Treatments
- Dialysis Access Procedures
- Vascular Malformations
- Carotid Disease
- Treating Leg Ulcers
- Treatment of Swollen Legs
- Vascular Trauma
- Portal Mesenteric Vascular Diseases
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Cervical Rib and Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Mesenteric Ischaemia

Dr. Gurunathreddy B
Vascular and Endovascular Surgeon
Vascular Malformations – FAQs
Common Questions, Clear Answers
Get clarity on what vascular malformations are, how they
behave, and when treatment is needed.
These FAQs help patients and families make informed decisions.
-
Simple explanations of complex vessel conditions
-
Guidance on when to seek specialist evaluation

If you have any other
questions about vascular malformations, please
contact us here
Are vascular malformations cancerous?
No, vascular malformations are not cancers. They are abnormal formations of blood or lymphatic vessels that are usually present from birth. However, they can enlarge, bleed, or cause symptoms over time, so proper diagnosis and monitoring are important.
Do all vascular malformations need treatment?
Not always. Small, asymptomatic malformations may simply be observed over time. Treatment is recommended if there is pain, swelling, bleeding, cosmetic concern, functional limitation, or risk of complications. Your specialist will advise based on symptoms and imaging findings.
What is sclerotherapy and how does it help?
Sclerotherapy involves injecting a special medication directly into the abnormal vessels to irritate and close them. Over time, the malformation shrinks and symptoms such as pain and swelling improve. It is commonly used for venous and some lymphatic malformations.
Is treatment for vascular malformations permanent?
Many patients experience long-lasting relief after treatment, but some malformations can recur or require staged procedures, especially if they are extensive or deep. Regular follow-up helps detect early changes and plan additional sessions if needed to maintain the best outcome.
