Treatment of Swollen Legs: Identifying the Cause and Restoring Comfort
Swollen legs and feet (leg oedema) are common symptoms that can range from mild discomfort to a sign of serious underlying vascular or medical conditions. Swelling may be due to venous insufficiency, lymphatic problems, deep vein thrombosis (DVT), heart, kidney, or liver disease, or prolonged standing or sitting. A proper vascular evaluation helps determine the cause and guides effective treatment to relieve symptoms and protect long-term limb health.
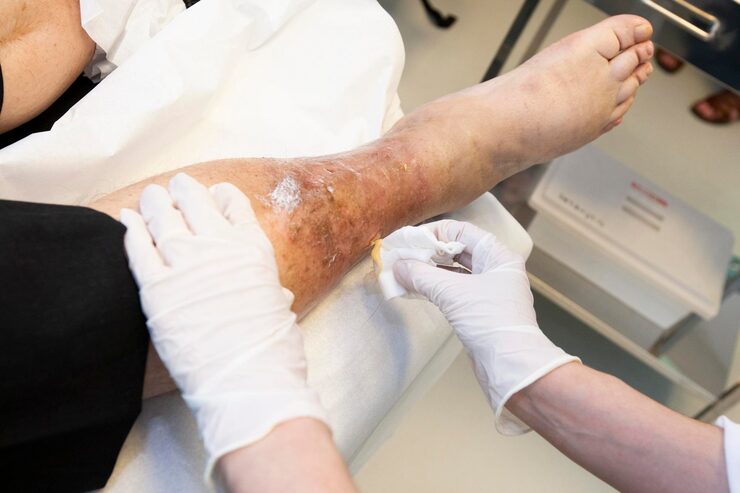
Common Causes of Swollen Legs
Swelling is not a disease by itself, but a symptom. Common vascular and systemic causes include:
- Chronic Venous Insufficiency: Weak or damaged leg veins causing blood pooling and swelling.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Blood clots in deep veins leading to painful, sudden swelling.
- Lymphoedema: Blockage or damage in the lymphatic system causing persistent, heavy swelling.
- Heart, Kidney, or Liver Disease: Fluid retention leading to bilateral leg swelling.
- Medications, Obesity, Pregnancy, or Prolonged Standing/Sitting can also contribute.
Symptoms Associated with Swollen Legs
- Heaviness, tightness, or discomfort in the legs or ankles.
- Visible varicose veins or skin colour changes.
- Indentation when pressing the skin (pitting oedema) in some cases.
- Redness, warmth, or pain suggesting infection or DVT.
- Thickened skin, recurrent infections, or non-healing wounds in chronic cases.
Diagnosis
A detailed history, examination, and investigations help identify the exact cause of swelling:
- Doppler Ultrasound: Assesses venous reflux, valve function, and rules out DVT.
- Arterial Studies / ABI: Evaluate blood flow in arteries, especially in PAD.
- Lymphatic Imaging (if required): To assess lymphatic obstruction.
- Blood Tests & Organ Evaluation: Check kidney, liver, and heart function.
Treatment Options
1. Lifestyle & Conservative Measures
- Leg elevation and avoiding prolonged standing or sitting.
- Weight management and regular walking or calf exercises.
- Reducing salt intake to minimise fluid retention.
2. Compression Therapy
- Medical-grade compression stockings to improve venous and lymphatic return.
- Multi-layer compression bandaging for severe oedema or venous ulcers.
3. Medications
- Diuretics (where appropriate) for fluid overload due to heart or kidney disease.
- Venoactive drugs and anti-inflammatory medication in selected patients.
- Anticoagulants for confirmed DVT as per specialist guidance.
4. Vascular & Lymphatic Procedures
- Endovenous ablation or surgery for significant venous insufficiency or varicose veins.
- Interventions to treat venous obstruction or DVT-related complications.
- Specialised lymphoedema therapy, physiotherapy, and in some cases, surgical options.
Why Early Evaluation of Swollen Legs Is Important
Persistent or unexplained leg swelling should never be ignored. It may be the first sign of venous disease, DVT, lymphoedema, or heart and kidney problems. Early diagnosis allows targeted treatment, prevents complications like ulcers, infections, and chronic pain, and greatly improves quality of life.
Our vascular specialists offer comprehensive evaluation and personalised treatment plans for swollen legs, combining advanced diagnostics, lifestyle guidance, and minimally invasive procedures when needed. If you are experiencing persistent swelling, heaviness, or discomfort in your legs, book a consultation to identify the cause and receive the right treatment.
Leg Swelling Treatment in HSR Layout – Advanced Vascular Care
Persistent leg swelling can indicate underlying vascular issues. At our Leg swelling treatment in HSR Layout clinic, we provide advanced diagnostics and minimally invasive treatments to improve circulation, reduce discomfort, and prevent complications. Our expert vascular specialists design personalized treatment plans using Doppler imaging, compression therapy, and lifestyle guidance for optimal recovery.
More Services
- Understanding Varicose Veins
- Lower Limb Arterial Diseases (PAD)
- Endovascular Treatments
- Dialysis Access Procedures
- Vascular Malformations
- Carotid Disease
- Treating Leg Ulcers
- Treatment of Swollen Legs
- Vascular Trauma
- Portal Mesenteric Vascular Diseases
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Cervical Rib and Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Mesenteric Ischaemia

Dr. Gurunathreddy B
Vascular and Endovascular Surgeon
Treatment of Swollen Legs – FAQs
Common Questions, Clear Answers
Learn why legs swell, when it is serious, and how vascular treatment can help. These FAQs provide practical guidance for patients and caregivers.
-
Understand when leg swelling needs urgent evaluation
-
Know how lifestyle changes and procedures work together

If you have persistent
swelling, pain, or heaviness
in your legs, contact us here
When is leg swelling a serious problem?
Sudden swelling in one leg, especially with pain, redness, or warmth, may indicate a deep vein thrombosis and requires urgent medical attention. Progressive swelling, skin changes, or recurrent infections also need evaluation by a vascular specialist.
Can swollen legs be treated at home?
Mild swelling from long hours of standing or sitting can improve with leg elevation, movement, and reduced salt intake. However, persistent or unexplained swelling should not be self-treated alone. A medical evaluation is important to rule out venous, lymphatic, or organ-related causes.
Do I need tests if both legs are swollen?
Yes. Swelling in both legs may suggest systemic conditions such as heart, kidney, or liver disease, or severe venous insufficiency. Your doctor may advise Doppler studies, blood tests, and imaging to determine the cause and start appropriate treatment.
Will compression stockings help my swollen legs?
Compression stockings are very helpful for venous insufficiency and some types of lymphoedema, but they must be used correctly and only after arterial circulation has been assessed. Your vascular specialist will recommend the right compression level and usage based on your condition.
