Carotid Artery Disease: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Carotid artery disease occurs when the carotid arteries—the major blood vessels on either side of the neck that supply oxygen-rich blood to the brain—become narrowed or blocked. This usually happens due to plaque buildup (atherosclerosis), which reduces blood flow and significantly increases the risk of stroke. Because carotid artery disease often develops silently, early diagnosis and timely treatment are critical.
What Causes Carotid Artery Disease?
The primary cause is atherosclerosis—a buildup of fatty deposits, cholesterol, calcium, and other substances inside the artery walls. Over time, this plaque hardens and narrows the arteries, lowering blood flow to the brain. Risk factors include:
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and accelerates plaque buildup.
- High Blood Pressure: Increases stress on artery walls.
- High Cholesterol: Promotes plaque formation.
- Diabetes: Causes inflammation and arterial damage.
- Obesity & Physical Inactivity
- Age & Family History: Risk increases over time.
Signs and Symptoms
Carotid artery disease may not show symptoms until it becomes advanced. Warning signs include:
- Transient Ischemic Attack (TIA): Temporary blockage of blood flow causing sudden weakness, numbness, slurred speech, vision issues, or dizziness.
- Stroke: A complete interruption of blood flow leading to paralysis, confusion, severe headache, or loss of consciousness. This is a medical emergency.
Diagnosing Carotid Artery Disease
Early detection reduces the risk of stroke. Diagnostic tools include:
- Carotid Ultrasound: Detects narrowing or blockages.
- CT / MRI Angiography: Provides detailed imaging of carotid arteries.
- Cerebral Angiography: A dye-based imaging test for precise assessment.
Treatment Options
1. Lifestyle Changes
- Quit smoking to prevent further artery damage.
- Follow a heart-healthy, low-fat diet.
- Exercise regularly to improve circulation.
2. Medications
- Antiplatelet drugs (Aspirin, Clopidogrel) to prevent clots.
- Statins to lower cholesterol and stabilize plaque.
- Blood pressure medications to reduce strain on arteries.
3. Surgical & Minimally Invasive Procedures
- Carotid Endarterectomy (CEA): Surgical removal of plaque to restore blood flow.
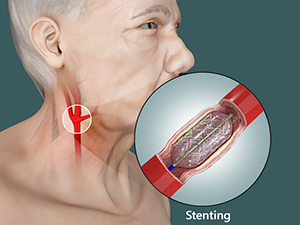
- Carotid Artery Stenting (CAS): A minimally invasive procedure where a stent is placed to widen the artery and keep it open.
Preventing Carotid Artery Disease
Although age and family history cannot be controlled, adopting a healthy lifestyle greatly reduces your risk. Prevention includes:
- Quit smoking and avoid secondhand smoke.
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to strengthen cardiovascular health.
- Manage blood pressure, cholesterol, and diabetes.
- Schedule regular check-ups and screenings.
Carotid artery disease is a major cause of stroke, which can lead to long-term disability or death. Early diagnosis and treatment significantly reduce the risk and help protect brain function. Our vascular specialists offer advanced diagnostics and personalised treatment options to help you maintain a healthy, stroke-free life.
Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment in Jayanagar – Advanced Vascular Care
Our Carotid Artery Stenosis Treatment in Jayanagar offers safe and minimally invasive care to restore proper blood flow in the carotid arteries. Sugathi Liver & Vascular Clinic provides advanced imaging, endovascular stenting, and surgical options to prevent strokes and improve vascular health. Our expert team ensures personalized care, faster recovery, and long-term outcomes for patients with arterial narrowing.
More Services
- Understanding Varicose Veins
- Lower Limb Arterial Diseases (PAD)
- Endovascular Treatments
- Dialysis Access Procedures
- Vascular Malformations
- Carotid Disease
- Treating Leg Ulcers
- Treatment of Swollen Legs
- Vascular Trauma
- Portal Mesenteric Vascular Diseases
- Aortic Aneurysm
- Diabetic Foot Ulcer
- Understanding Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Cervical Rib and Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Peripheral Vascular Disease
- Mesenteric Ischaemia

Dr. Gurunathreddy B
Vascular and Endovascular Surgeon
Carotid Artery Disease – FAQs
Common Questions, Clear Answers
Learn how carotid artery disease develops, how to detect stroke warning signs, and what treatment options are available. These FAQs help you take timely action.
-
Understand symptoms before they progress into a stroke
-
Know your treatment choices and when surgical care is needed

If you have any concerns or
symptoms related to stroke or
carotid disease, contact us here
Is carotid artery disease dangerous?
Yes. Carotid artery disease is one of the leading causes of stroke, a life-threatening condition that can cause permanent brain damage, disability, or death. Early detection and treatment reduce these risks significantly.
Can carotid artery disease be detected early?
Yes. A simple carotid ultrasound can detect narrowing even before symptoms appear. People with risk factors such as high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, or high cholesterol should undergo periodic screening.
Is surgery always required to treat carotid artery disease?
Not always. Mild to moderate narrowing may be managed with medications and lifestyle changes. Surgery or stenting is recommended only when blockages are significant or when symptoms such as TIA or stroke occur.
How can I reduce my risk of stroke from carotid disease?
Stop smoking, control blood pressure and cholesterol, follow a heart-healthy diet, exercise regularly, manage diabetes, and attend regular screenings. Recognising early warning signs such as sudden numbness, vision loss, or difficulty speaking is critical for immediate care.
